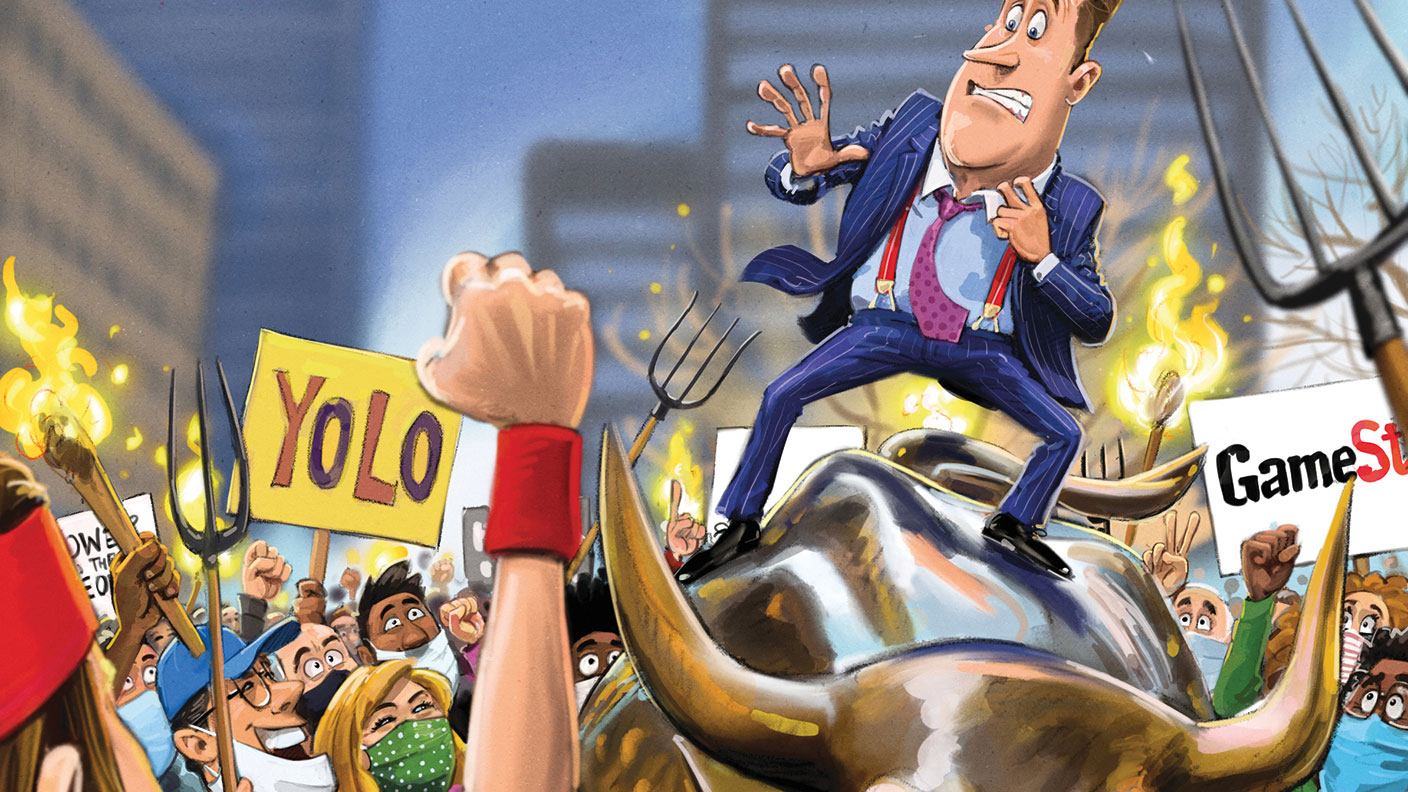
GameStop, short-sellers, Reddit rebels and Wall Street’s wonky plumbing
What was the furore over US retailer GameStop really about? Is silver the next big social media-driven trade? And what does any of this mean for sensible long-term investors? John Stepek tries to unravel the story.


Get the latest financial news, insights and expert analysis from our award-winning MoneyWeek team, to help you understand what really matters when it comes to your finances.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Twice daily
MoneyWeek
Get the latest financial news, insights and expert analysis from our award-winning MoneyWeek team, to help you understand what really matters when it comes to your finances.

Four times a week
Look After My Bills
Sign up to our free money-saving newsletter, filled with the latest news and expert advice to help you find the best tips and deals for managing your bills. Start saving today!
In short, not very. One angle that has been pored over and amplified by many in the press is the idea that Reddit users are angry about 2008. We’ve already noted above that the “rebellion” started as a value investing thesis, but some posts on the website do point to a generalised anger about bailouts in 2008 and a re-run of “Occupy Wall Street”. Yet hedge funds and short-sellers are the wrong target for this rage against “too big to fail”.
As Michael Lewis’s book, The Big Short (and the film of the same name) explain, short-sellers were among the few institutions to spot and warn of the risks in the housing market in 2008. Moreover, short-sellers were not bailed out at any point during the financial crisis – it was the banks who were saved (which was arguably the right thing to do at the time, though you can certainly argue with the way it was done and the relative lack of consequences for those who were in charge).
So what good do short-sellers do? In return for taking the risk of uncapped losses, they’ve helped to uncover frauds ranging from Enron in 2001 to Wirecard last year (those who think this should be the job of the authorities should note that the German regulator tried to have Financial Times journalists arrested for pursuing the latter story). But what of the “good, honest” companies that short-sellers have bankrupted? I’ve tried to uncover even one example of this, yet while lots of people clearly feel very hostile towards short-sellers (just try defending them on Twitter), they can’t point to any specifics to back up their views – so email editor@moneyweek.com if you have an example.
MoneyWeek
Subscribe to MoneyWeek today and get your first six magazine issues absolutely FREE

Sign up to Money Morning
Don't miss the latest investment and personal finances news, market analysis, plus money-saving tips with our free twice-daily newsletter
Don't miss the latest investment and personal finances news, market analysis, plus money-saving tips with our free twice-daily newsletter
Get the latest financial news, insights and expert analysis from our award-winning MoneyWeek team, to help you understand what really matters when it comes to your finances.

-
 ISA fund and trust picks for every type of investor – which could work for you?
ISA fund and trust picks for every type of investor – which could work for you?Whether you’re an ISA investor seeking reliable returns, looking to add a bit more risk to your portfolio or are new to investing, MoneyWeek asked the experts for funds and investment trusts you could consider in 2026
-
 The most popular fund sectors of 2025 as investor outflows continue
The most popular fund sectors of 2025 as investor outflows continueIt was another difficult year for fund inflows but there are signs that investors are returning to the financial markets
-
 Three companies with deep economic moats to buy now
Three companies with deep economic moats to buy nowOpinion An economic moat can underpin a company's future returns. Here, Imran Sattar, portfolio manager at Edinburgh Investment Trust, selects three stocks to buy now
-
 Should you sell your Affirm stock?
Should you sell your Affirm stock?Affirm, a buy-now-pay-later lender, is vulnerable to a downturn. Investors are losing their enthusiasm, says Matthew Partridge
-
 Why it might be time to switch your pension strategy
Why it might be time to switch your pension strategyYour pension strategy may need tweaking – with many pension experts now arguing that 75 should be the pivotal age in your retirement planning.
-
 Beeks – building the infrastructure behind global markets
Beeks – building the infrastructure behind global marketsBeeks Financial Cloud has carved out a lucrative global niche in financial plumbing with smart strategies, says Jamie Ward
-
 Saba Capital: the hedge fund doing wonders for shareholder democracy
Saba Capital: the hedge fund doing wonders for shareholder democracyActivist hedge fund Saba Capital isn’t popular, but it has ignited a new age of shareholder engagement, says Rupert Hargreaves
-
 Silver has seen a record streak – will it continue?
Silver has seen a record streak – will it continue?Opinion The outlook for silver remains bullish despite recent huge price rises, says ByteTree’s Charlie Morris
-
 Investing in space – finding profits at the final frontier
Investing in space – finding profits at the final frontierGetting into space has never been cheaper thanks to private firms and reusable technology. That has sparked something of a gold rush in related industries, says Matthew Partridge
-
 Star fund managers – an investing style that’s out of fashion
Star fund managers – an investing style that’s out of fashionStar fund managers such as Terry Smith and Nick Train are at the mercy of wider market trends, says Cris Sholto Heaton