The case for nickel – a crucial metal in the Green Energy Revolution
Nickel’s use in batteries for electric vehicles makes it a vital metal for the 21st century. Dominic Frisby investigates how to invest.


Get the latest financial news, insights and expert analysis from our award-winning MoneyWeek team, to help you understand what really matters when it comes to your finances.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?
“Tesla will give you a giant contract for a long period of time if you mine nickel efficiently and in an environmentally sensitive way,” said Tesla CEO Elon Musk in July 2020.
In September he reiterated his position: “In order to scale, we really need to make sure that we’re not constrained by total nickel availability. I spoke with the CEO of the biggest mining company in the world and said, ‘Please make more nickel, it’s very important.’”
One year on from those big statements, we consider the investment case for nickel.
Try 6 free issues of MoneyWeek today
Get unparalleled financial insight, analysis and expert opinion you can profit from.

Sign up to Money Morning
Don't miss the latest investment and personal finances news, market analysis, plus money-saving tips with our free twice-daily newsletter
Don't miss the latest investment and personal finances news, market analysis, plus money-saving tips with our free twice-daily newsletter
Nickel wants to go higher
Nickel, like all metals, has had quite a time of it over the last few years. Today it trades around US$19,500/tonne – a seven-year high.
The lows came in 2015-2016 – and, short of some kind of deflationary bust – I doubt we’ll ever see them again. We didn’t even touch them during the March 2020 Covid panic. Those lows were around $8,000/tonne.
However, the all-time high for nickel came in May 2007. It perhaps marked peak mania towards the end of the last great commodity supercycle. $54,300 was the price, so we are still some way off that.
If I look at a short-term chart of nickel I have to say I am not greatly encouraged by the price action. We hit a high in February, re-tested it last week and failed, and since then the price has been sliding.
However, if I look at a longer-term chart, I see a huge base that has formed over many years, with consistently higher lows since 2016, and that now looks like it wants to go higher, a lot higher. We are a long way from the speculative manias you find at the end of large bull markets.
Here’s a screenshot from the London Metals Exchange (LME) – what do you make of it?
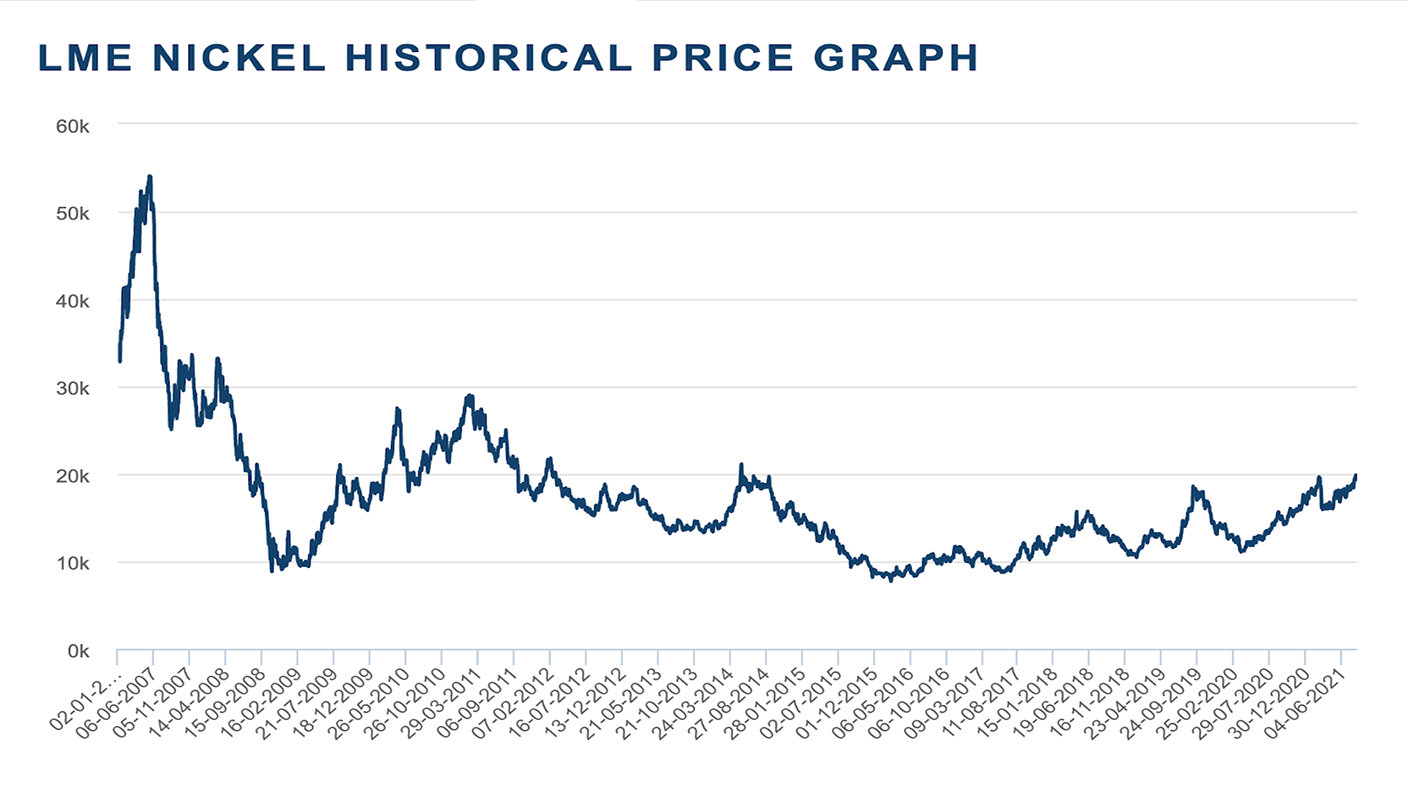
Perhaps we just need to digest and consolidate the gains of the past year for a little longer before the bull market can get going again. Summer doldrums and all that.
Nickel’s role in the Green Energy Revolution
Nickel is the fifth most common element on earth. Humans have been using it since the bronze age, but it wasn’t officially recognised until 1751. Ancient Chinese manuscripts refer to “white copper”, while northern European miners in the Middle Ages called it Kupfernickel, which translates as “Old Nick’s copper” or “devil’s copper”, because the reddish ore looked like copper, but they couldn’t get any copper out of it.
Nickel has a high melting point, resists corrosion and oxidation, is ductile, magnetic at room temperature and alloys readily. It can be deposited by electroplating, has catalytic properties and recycles well – it can be re-used again and again. With these properties, its biggest use by far – almost 80% of annual demand – is in stainless steel. The rest comes from alloys (10%), plating (4%), electric vehicle batteries (3%) and, of course, “other”. Nickel use has been growing at a rate of about 4% per annum since 2010.
The excitement around the metal lies in its use in electric vehicle (EV) batteries. Nickel is a key component for EV cathodes. “Green energy will play a key role in nickel’s future,” says the LME. “The rapid rise of electric vehicles and growing importance of battery technology are likely to increase demand for higher purity nickel. Whilst EV’s only represent a small share of the current nickel story, government policy and the strategic plans of well-known automotive players are driving the renewable automotive manufacturing, and in turn a small part of the energy industry forward, which will impact the nickel futures market.”
It’s that Green Energy Revolution again, and the huge demands it places on natural resources.
Demand from electric vehicles is small – but that will change
Eddy Haegel, president of BHP Nickel West, said this week: “We believe that over 2020 to 2030, overall nickel demand will grow at 5% compound annual growth rate, and that nickel-in-battery demand will grow at a rate of 21% CAGR.” He sees EVs accounting for 25% of all vehicles sold by 2030.
Meanwhile, we have Elon Musk saying, “Please make more nickel, it’s very important.” Musk likes the greater energy density of nickel-rich, cobalt-free cathodes. That’s why he wants nickel. Robyn Denholm, chair of Tesla, says it will purchase around $1bn per year in battery minerals from Australia alone.
Nickel demand in the EV and energy storage sectors remains relatively small, but the outlook is that this will change. The International Energy Agency estimates a rise of 4,000% over the next 20 years — “from 81 metric tons in 2020 to 3,352 metric tons by 2040”. How they can be quite so precise, I’ve no idea, but one presumes there is a methodology.
80% of all nickel historically mined, says the Nickel Institute, was extracted over the past three decades. Worldwide, around 2.5 million tonnes of nickel are mined per year, according to this year’s US geological survey. Indonesia (760,000 tonnes) is the world’s biggest producer, followed by the Philippines (320,000 tonnes), Russia (280,000 tonnes), New Caledonia (200,000 tonnes), Australia (170,000 tonnes) and Canada (150,000 tonnes).
The world’s nickel resources are currently estimated at 300 million tonnes, and there are thought to be significant deposits in the deep sea, which no doubt humans will eventually start mining (if they don’t get to outer space first).
The world’s biggest producers are Vale, Norilsk Nickel, Jinchuan Group International Resources, Glencore and BHP Group – the latter two being the simplest option for UK investors. But they are far from pure plays: BHP’s nickel division accounts for less than 1% of its earnings.
The small and mid-cap pure plays are where the big nickel bucks will be made – and lost.
Get the latest financial news, insights and expert analysis from our award-winning MoneyWeek team, to help you understand what really matters when it comes to your finances.

-
 Financial education: how to teach children about money
Financial education: how to teach children about moneyFinancial education was added to the national curriculum more than a decade ago, but it doesn’t seem to have done much good. It’s time to take back control
-
 Investing in Taiwan: profit from the rise of Asia’s Silicon Valley
Investing in Taiwan: profit from the rise of Asia’s Silicon ValleyTaiwan has become a technology manufacturing powerhouse. Smart investors should buy in now, says Matthew Partridge
-
 Key lessons from the MoneyWeek Wealth Summit 2025: focus on safety, value and growth
Key lessons from the MoneyWeek Wealth Summit 2025: focus on safety, value and growthOur annual MoneyWeek Wealth Summit featured a wide array of experts and ideas, and celebrated 25 years of MoneyWeek
-
 The Stella Show is still on the road – can Stella Li keep it that way?
The Stella Show is still on the road – can Stella Li keep it that way?Stella Li is the globe-trotting ambassador for Chinese electric-car company BYD, which has grown into a world leader. Can she keep the motor running?
-
 Tesla seeks approval to supply electricity to UK homes – could it disrupt the energy market?
Tesla seeks approval to supply electricity to UK homes – could it disrupt the energy market?Tesla has applied for a license to supply UK households with electricity, but taking on the biggest providers could prove challenging
-
 Tesla shares slump over Trump/Musk feud
Tesla shares slump over Trump/Musk feudA war of words has sent Tesla shares spiralling to the company’s largest single-day value decline in history
-
 Tesla is no longer the world’s largest electric car maker. Should you invest?
Tesla is no longer the world’s largest electric car maker. Should you invest?Investors need to weigh up the potential of Tesla’s autonomous technology drive against struggles in its core carmaking business when deciding whether or not to invest
-
 Amazon shares fall on profitability concerns
Amazon shares fall on profitability concernsA big increase in capital spending plans compounded an earnings miss for Amazon following its Q4 results
-
 Halifax: House price slump continues as prices slide for the sixth consecutive month
Halifax: House price slump continues as prices slide for the sixth consecutive monthUK house prices fell again in September as buyers returned, but the slowdown was not as fast as anticipated, latest Halifax data shows. Where are house prices falling the most?
-
 Rents hit a record high - but is the opportunity for buy-to-let investors still strong?
Rents hit a record high - but is the opportunity for buy-to-let investors still strong?UK rent prices have hit a record high with the average hitting over £1,200 a month says Rightmove. Are there still opportunities in buy-to-let?