Can The Gym Group pump up your portfolio?
The Gym Group was one of the best UK small-cap stocks in 2024


Get the latest financial news, insights and expert analysis from our award-winning MoneyWeek team, to help you understand what really matters when it comes to your finances.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Twice daily
MoneyWeek
Get the latest financial news, insights and expert analysis from our award-winning MoneyWeek team, to help you understand what really matters when it comes to your finances.

Four times a week
Look After My Bills
Sign up to our free money-saving newsletter, filled with the latest news and expert advice to help you find the best tips and deals for managing your bills. Start saving today!
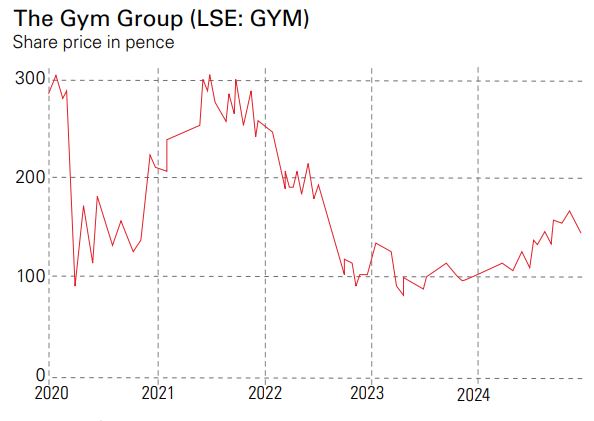
The Gym Group (LSE: GYM) has recorded one of the best performances among UK small caps in 2024. The stock has returned around 42% over the year and at one point had gained almost 65%. The FTSE All-Share has returned less than 10% year to date. Even after this performance, the shares in the low-cost gym operator look cheap compared with its growth potential and cash generation.
The Gym Group's growth streak
The fitness and leisure market in the UK has recorded an impressive growth streak over the past five years. The number of gyms across the country remains below the pre-pandemic peak of 7,239, but the number of members has reached a record – 15.9% of the UK population are now members, up from 15.6% in 2019.
The number of overall gym members rose 4.1% in 2023 to 10.7 million, according to the State of the UK Fitness Industry Report 2024, compiled by market intelligence expert Leisure DB. At the same time, the number of public-sector gyms has steadily declined since 2019, as high energy costs and council budget pressures have forced closures. These tailwinds have helped drive the Gym Group’s growth since 2019. It lost around one in five of its members during the Covid lockdowns of 2020 and burnt through as much as £6 million a month as its gyms were forced to close. But when the economy reopened, the firm bounced back, with operating cash flow (before capital spending) returning to the black in 2021.
MoneyWeek
Subscribe to MoneyWeek today and get your first six magazine issues absolutely FREE

Sign up to Money Morning
Don't miss the latest investment and personal finances news, market analysis, plus money-saving tips with our free twice-daily newsletter
Don't miss the latest investment and personal finances news, market analysis, plus money-saving tips with our free twice-daily newsletter
The company isn’t the largest operator of low-cost gyms in the country (that title belongs to peer PureGym, which operates 400 gyms), but its size and scale give it a considerable edge. Over the past five years, the group has raised the number of its locations by 44%, from 165 gyms in 2019 to 237 gyms in 2024.
In early 2024, the group announced an agreement with real-estate adviser Savills to help it select locations as part of a plan to open 50 new sites across the UK in the next three years. PwC suggests there’s scope for 600-800 more sites in the low-cost segment by the end of the decade. Site selection is key to the Gym Group’s model. The firm is looking for highly visible locations with easy access to parking or close proximity to transport links, as its members prioritise convenience and locality. It’s also looking for value, and these twin goals have pushed the company towards unloved and unwanted high-street retail units, which it has been getting for attractive rents.
The company is self-funding this growth with cash flow generated from operations. Free cash flow after growth capital expenditures turned positive in 2023 and the company has said it plans to maintain this stance going forward. Notably, its return on invested capital (ROIC), a measure of profit for every £1 invested in the business, stands at more than 30%, an impressive return for a business that has to invest millions in each gym before opening.
What's behind The Gym Group's success?
The Gym Group’s secret sauce is volume and sticky recurring revenue. Across 237 gyms, the company has an average of 905,000 members, or 3,820 per gym. How can a gym typically 10,000-20,000 square feet (roughly the same as a medium-sized industrial unit) take 3,820 members? It can’t, and it doesn’t. If every member turned up at the gym at once, in a 10,000 sq ft space, they’d have less than three square feet to use, leaving no space for equipment, changing rooms, and so on. But according to PureGym’s UK Fitness Report 2025, only 10% of people who exercise regularly do so every day and only 40% exercise two to three times per week (exercise, in this case, includes all forms of activity, not just a session in the gym). Other data reinforces this point, suggesting the average number of times a gym member visits for a workout is around twice a week, with an average duration of approximately an hour. Additionally, the average membership term is around 14 months, with members more likely to stay if they make it through the first few months.
The Gym Group relies heavily on these passive users to subsidise regular gym-goers and its growth plans. The number of users signed up for each of the group’s gyms has remained relatively constant over the past five years, suggesting there is a ceiling for the number of members per gym, although this is most likely a side effect of the group’s strategy of focusing on convenience and locality.
The Gym Group's membership model
The other part of the group’s strategy is price growth. Since 2019, the Gym Group has increased its “standard” monthly membership fees while reducing promotions and adding new membership tiers, such as “ultimate” and “off-peak”. As a result, the average revenue per member per month has risen from £15.47 in 2019 to £20.44 in 2024. There’s room for further growth here as well. The Leisure DB’s State of the UK Fitness Report 2024 showed that, despite recent price hikes, a gap remains of £1.58 between the Gym Group and PureGym.
In spite of the attractive fundamentals and growth outlook, the firm is still undervalued. According to Panmure Liberum, the firm is currently trading at an enterprise value of £1.3 million per gym, below the estimated construction cost of £1.4 million, which would make sense if each gym was losing money, which it isn’t. The ROIC of 30% makes that quite clear.
The stock is trading on a free cash flow yield of 11.9% and an enterprise value to earnings before interest, tax, depreciation and amortisation (EV/Ebitda) ratio of 7.5 times, compared with 9.1 times in 2019, according to Panmure Liberum. The City has placed an average price target of 190p a share on the stock, around 32% above current levels. Considering these metrics, that looks conservative.
This article was first published in MoneyWeek's magazine. Enjoy exclusive early access to news, opinion and analysis from our team of financial experts with a MoneyWeek subscription.
Get the latest financial news, insights and expert analysis from our award-winning MoneyWeek team, to help you understand what really matters when it comes to your finances.

Rupert is the former deputy digital editor of MoneyWeek. He's an active investor and has always been fascinated by the world of business and investing. His style has been heavily influenced by US investors Warren Buffett and Philip Carret. He is always looking for high-quality growth opportunities trading at a reasonable price, preferring cash generative businesses with strong balance sheets over blue-sky growth stocks.
Rupert has written for many UK and international publications including the Motley Fool, Gurufocus and ValueWalk, aimed at a range of readers; from the first timers to experienced high-net-worth individuals. Rupert has also founded and managed several businesses, including the New York-based hedge fund newsletter, Hidden Value Stocks. He has written over 20 ebooks and appeared as an expert commentator on the BBC World Service.
-
 How a ‘great view’ from your home can boost its value by 35%
How a ‘great view’ from your home can boost its value by 35%A house that comes with a picturesque backdrop could add tens of thousands of pounds to its asking price – but how does each region compare?
-
 What is a care fees annuity and how much does it cost?
What is a care fees annuity and how much does it cost?How we will be cared for in our later years – and how much we are willing to pay for it – are conversations best had as early as possible. One option to cover the cost is a care fees annuity. We look at the pros and cons.
-
 Three key winners from the AI boom and beyond
Three key winners from the AI boom and beyondJames Harries of the Trojan Global Income Fund picks three promising stocks that transcend the hype of the AI boom
-
 RTX Corporation is a strong player in a growth market
RTX Corporation is a strong player in a growth marketRTX Corporation’s order backlog means investors can look forward to years of rising profits
-
 Profit from MSCI – the backbone of finance
Profit from MSCI – the backbone of financeAs an index provider, MSCI is a key part of the global financial system. Its shares look cheap
-
 'AI is the real deal – it will change our world in more ways than we can imagine'
'AI is the real deal – it will change our world in more ways than we can imagine'Interview Rob Arnott of Research Affiliates talks to Andrew Van Sickle about the AI bubble, the impact of tariffs on inflation and the outlook for gold and China
-
 Should investors join the rush for venture-capital trusts?
Should investors join the rush for venture-capital trusts?Opinion Investors hoping to buy into venture-capital trusts before the end of the tax year may need to move quickly, says David Prosser
-
 Food and drinks giants seek an image makeover – here's what they're doing
Food and drinks giants seek an image makeover – here's what they're doingThe global food and drink industry is having to change pace to retain its famous appeal for defensive investors. Who will be the winners?
-
 Barings Emerging Europe trust bounces back from Russia woes
Barings Emerging Europe trust bounces back from Russia woesBarings Emerging Europe trust has added the Middle East and Africa to its mandate, delivering a strong recovery, says Max King
-
 How a dovish Federal Reserve could affect you
How a dovish Federal Reserve could affect youTrump’s pick for the US Federal Reserve is not so much of a yes-man as his rival, but interest rates will still come down quickly, says Cris Sholto Heaton