Corporate bonds look costly: but these two risky plays might pay off
Corporate bonds have been very popular investments of late - but they are now looking expensive. Phil Oakley asks whether there is any value left in them, and picks two risky but potentially lucrative bonds to buy now.
Get the latest financial news, insights and expert analysis from our award-winning MoneyWeek team, to help you understand what really matters when it comes to your finances.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Twice daily
MoneyWeek
Get the latest financial news, insights and expert analysis from our award-winning MoneyWeek team, to help you understand what really matters when it comes to your finances.

Four times a week
Look After My Bills
Sign up to our free money-saving newsletter, filled with the latest news and expert advice to help you find the best tips and deals for managing your bills. Start saving today!
Investors' love affair with corporate bonds shoes no sign of waning. It's not hard to see why: they have produced decent returns during the last few years. Over the last year alone, UK corporate bonds have risen by 11% compared to the FTSE 100 which is virtually unchanged (excluding dividends).
But should you still be buying them now? We're not so sure.
Why corporate bonds have done so well
In simple form, a corporate bond represents part of a company's debt sold to investors. They are usually sold in batches of £100 each, and the company promises to pay a rate of interest over the life of the bond, then repay the £100 at the end.
MoneyWeek
Subscribe to MoneyWeek today and get your first six magazine issues absolutely FREE

Sign up to Money Morning
Don't miss the latest investment and personal finances news, market analysis, plus money-saving tips with our free twice-daily newsletter
Don't miss the latest investment and personal finances news, market analysis, plus money-saving tips with our free twice-daily newsletter
The great thing about corporate bonds is that they pay higher interest rates than government bonds. They also pay investors before shareholders. This makes them less risky than shares, which is one reason why investors like them.
It has also become a lot easier for private investors to buy and sell corporate bonds in recent years. This has created additional demand.
However, as with government bonds, the main driver of the corporate bond bull market has been falling interest rates. As central banks have printed money, bond prices have risen and their yields have fallen. The prices and yields of corporate bonds have done the same.
Corporate bonds now look expensive
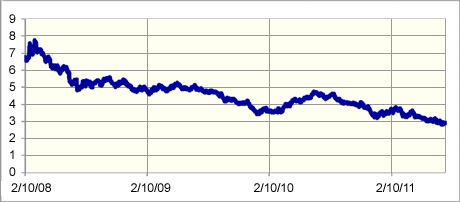
Have a look at the chart below. It shows the redemption yield on a Safeway (now owned by Morrisons) corporate bond.
As you can see, in late 2008 at the time of the financial crisis you could have bought this bond with a yield of more than 7%. From an income point of view, that looks to have been a pretty good buy.
On top of that, the price of the bond has gone from £89 to £119 an increase of 34%. That's left the yield at 3%. That's not so attractive. And a similar scenario has played out for many corporate bonds.
Safeway 6.125% 2018 redemption yield
In fact, the redemption yields on many companies' corporate bonds are now lower - sometimes a lot lower - than the dividend yields on the their shares (see table below).
I have some sympathy for the view that the extra risk you take with shares (because you are last in the queue to get paid) suggests that their dividend yields should be higher than those of their corporate bonds.
However, if the dividends are capable of growing, they may be a better bet than the bonds, which generally have fixed coupons.
| Unilever | 4.75 | 2017 | 112.65 | 115.65 | 4.1% | 1.89% | 3.61% | 1.72% |
| United Utilities Water | 5.375 | 2018 | 112.3 | 114.8 | 4.7% | 2.92% | 4.90% | 1.98% |
| HSBC Holdings | 9.875 | 2018 | 105.35 | 110.35 | 8.9% | 2.34% | 4.70% | 2.36% |
| Safeway plc | 6.125 | 2018 | 117.4 | 120.4 | 5.1% | 3.00% | 3.60% | 0.60% |
| Marks Spencer | 6.125 | 2019 | 108.3 | 111.3 | 5.5% | 4.53% | 4.52% | 0.01% |
| Tesco | 5.5 | 2019 | 113.5 | 115.8 | 4.7% | 3.31% | 4.60% | 1.29% |
| BAT Intl Finance Plc | 6.375 | 2019 | 120.6 | 123.6 | 5.2% | 3.10% | 4.00% | 0.90% |
| SSE plc | 5.875 | 2022 | 116.35 | 119.35 | 4.9% | 3.75% | 5.80% | 2.05% |
| Severn Trent Water | 6.125 | 2024 | 118.5 | 122 | 5.0% | 3.93% | 4.10% | 0.17% |
| National Grid Gas | 8.75 | 2025 | 147 | 150.5 | 5.8% | 3.92% | 5.60% | 1.68% |
| Vodafone | 5.625 | 2025 | 116.9 | 119.9 | 4.7% | 3.83% | 5.20% | 1.37% |
Is there any value left in corporate bonds?
The truth is, we can't say for sure. A market might look expensive, but it can stay expensive for a long time.
What we do know is that investors seem to be paying quite a high price for the perceived safety of good quality corporate bonds.
Why buy Safeway corporate bonds with a yield of 3%, when you can buy shares in its parent company, Morrisons? It has a dividend yield of 3.6% with dividend growth of at least 10% expected for the next two years. And while the supermarket business is tough right now, Morrison's dividend cover is 2.4 times whilst debt levels are low.
So is there any real value left in corporate bonds? If you expect government bond yields to go any lower, then yes, there is. But given how low they are already, we're not sure just how much more can be eked out of the market.
However, if you are willing to take on a bit of risk, the following two bonds might be of interest:
Barclays Bank 5.75% 2026 at £89 per £100 has an income yield of 6.5% and a redemption yield of 7.1%.
Halifax 9.375% 2021 at £103 per £100 has an income yield of 9.1% and a redemption yield of 9%.
Both these bonds still retain investment grade credit ratings. They are also 'bullet' bonds, which means the company cannot redeem them before their maturity dates. Note that the Halifax bond is only tradeable in increments of £10,000 and so may only be suitable for large diversified portfolios. The Barclays bond can be traded in increments of £1,000.
We think the equity of banks such as Barclays and Lloyds (which owns Halifax) are very risky. The debt is still risky, but less so. One good reason for this is that these banks will be required to hold more equity in the future.
This will provide an extra buffer of safety for bondholders. Taking this on board, these bonds could represent decent - if risky - contrarian investments.
Get the latest financial news, insights and expert analysis from our award-winning MoneyWeek team, to help you understand what really matters when it comes to your finances.
Phil spent 13 years as an investment analyst for both stockbroking and fund management companies.
-
 Should you buy an active ETF?
Should you buy an active ETF?ETFs are often mischaracterised as passive products, but they can be a convenient way to add active management to your portfolio
-
 Power up your pension before 5 April – easy ways to save before the tax year end
Power up your pension before 5 April – easy ways to save before the tax year endWith the end of the tax year looming, pension savers currently have a window to review and maximise what’s going into their retirement funds – we look at how